大胆予測
キャリートレードの巻き戻しでUSD/JPYが100を下回り、日本に次なる資産バブルが到来
チャル・チャナナ
チーフ・インベストメント・ストラテジスト
Sales Trader
サマリー: カラー取引とは、投資家やトレーダーがオプションの売り買いを通じてポートフォリオのボラティリティを低下させるために利用できるオプション戦略のことである。これは、原資産のアップサイドとダウンサイドの両方を短期的に制限することで実現します。カラー・ポジションは、プロテクティブ・プット戦略とカバード・コール・オプション戦略の両方を同時に使用することにより形成されます。
カラー取引=現物株+アウト・オブ・ザ・マネーのプット・オプションの買い+アウト・オブ・ザ・マネーのコール・オプションの売り
この戦略は通常、短期的な下落リスクを懸念するトレーダーが使用する。トレーダーは、アウト・オブ・ザ・マネーのコール・オプションを売り、 同時に同じ原銘柄のアウト・オブ・ザ・マネーのプット・オプションを買うことで、ダウ ンサイド・プロテクションを購入するためのプレミアムを調達するためにアップサイドに キャップをつける。
アウト・オブ・ザ・マネーのコール・オプションの売りでは、株式の現在の取引価格より高い権利行使価格のコール・オプションを選択する(株式の取引価格は170ドル、コールの権利行使価格は180ドル)。アウト・オブ・ザ・マネーのプット・オプションを買うには、現在の株価より低い権利行使価格のプット・オプションを選ぶ(株価は170ドル、権利行使価格は160ドル)。
カラー取引は、短期的に株式の下落リスクをヘッジしたいが、短期的なリスクを恐れて株式を売却するつもりはないトレーダーのための選択肢である。そのため、コールオプションを売り、そのプレミアムでダウンサイドリスクに対するプロテクションを購入することで、利益に上限を設けることに抵抗がない。
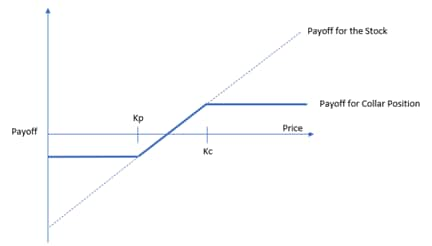
【例】
Kp = OTM(アウト・オブ・ザ・マネー)のプットオプションの権利行使価格
Kc = OTM (アウト・オブ・ザ・マネー)のコール・オプションの権利行使価格
これは、カラー・オプション戦略を使った場合のペイオフ・ダイアグラムである。株価がプット・オプションの権利行使価格 Kp を下回ると、トレーダー/投資家の損失は限定的となる。しかし、株価がコール・オプションの権利行使価格 Kc よりも上昇した場合、トレーダー/投資家の上昇幅は限定的となる。
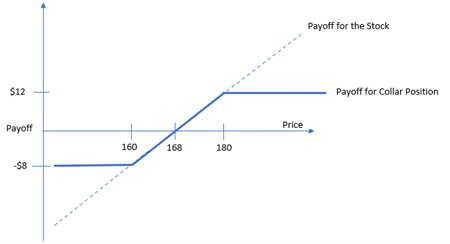
一株当たりの最大利益は、アップルが180ドルに上昇したとき
3ドル(コールオプションの売りで受け取ったプレミアム) - 1ドル(プットオプションの買いで支払ったプレミアム) + 10ドル(アップル株を所有することによる利益) = 12ドル
損益分岐点
170ドル + 3ドル(コールオプションの売りで受け取ったプレミアム) - 1ドル(プットオプションの買いで支払ったプレミアム) = 168ドル
アップルが160ドルを下回った場合の1株当たりの最大損失額
3ドル(コール・オプションの売りで受け取ったプレミアム) - 1ドル(プット・オプションの買いで支払ったプレミアム) - 10ドル(アップル株を所有することによる損失) = -8ドル
シナリオ 1 - アップルが 175 ドルまで取引された場合
損益 = $3(コールオプションの売りで受け取ったプレミアム) - $1(プットオプションの買いで支払ったプレミアム) + $5(アップル株の保有による利益) = 7ドル
シナリオ2 - アップルが165ドルに取引される
損益 = 3ドル(コールオプションの売りで受け取ったプレミアム) - 1ドル(プットオプションの買いで支払ったプレミアム) - 5ドル(アップル株の所有による損失) = -3ドル
カラー オプション戦略は、トレーダー/投資家のツールキットのもう 1 つの戦術オプションで、ポートフォリオ内のポジションを短期から中期にわたってヘッジするのに役立ちます。投資家が特定の株式で大きなポジションを保有している場合、その株式を手放すことなく、短期的な下落リスクから守るためにカラーポジションを構築できます。原資産の価格下落をヘッジするためのプロテクティブ・プット・オプションの購入コストは、カバード・コールのプレミアムで相殺できます。プット・オプションのコストがコール・オプションの売りで得るプレミアムによって全額カバーされる場合、これをゼロコスト・カラーと呼ぶことができます。プット・オプションのコストがコール・オプションの売りによって受け取るプレミアムよりも低い場合、これは部分的にヘッジおよび部分的に利回り向上戦略として機能します。
What is the Collar Option Strategy?
Collar Position = Underlying Stock + Long Out of The Money Put Option + Short Out of The Money Call Option
The strategy is typically used by traders who are holding are concerned about the downside risks in the short term. The traders sell an out of the money call option while simultaneously buying an out of the money put option on the same underlying stock thereby capping the upside in order to fund the premium to buy downside protection
Selling an out of the money call option involves choosing a call option with a strike higher than the current trading price of the stock ( Stock trading at $170, call strike at $180). Buying an out of the money put option involves choosing a put option with a strike below the current trading price of the stock (stock trading at $170, put strike at $160).
Why use the Collar Option Strategy?
Collar strategy is an alternative to traders who are looking to hedge the downside risks of the stocks in the short term but have no intention to sell the stock for the fear of short-term risks. Therefore they are comfortable to commit to capping their profits by selling the call option and using that premium to buy protection against downside risks.
Legend
Kp = Strike price for OTM put option
Kc = Strike price for OTM call option
This is the pay-off diagram for using a collar option strategy. The trader/investor would have limited losses when the price of the stock falls below the put option’s strike price of Kp. However, if the stock rises above the call option’s strike price of Kc, the trader/investor would have limited upside.
Example
A client owns 100 shares in Apple trading at the price of $170. He sells 1 call option at strike $180 with a 1 month expiry. At the same time, he also buys a put option at strike of $160. The premium received from selling the call option is $3 while the cost of buying the put option is $1. In this example, Apple call options are more expensive than put options (positive skew), implying that the market is pricing in a more bullish scenario for Apple. You would receive a net premium of $2 credit per share with this structure. If you wish to make this trade a zero-cost strategy, you can afford to buy a put option with a higher strike that cost up to $3. This would offer greater downside protection.
Max gain per share is when Apple rises to $180
$3 (premium received from selling call option) - $1 (premium paid for buying put option) + $10 ( gain from owning Apple shares) = $12
Breakeven point
$170 + $3 (premium received from selling call option) - $1 (premium paid for buying put option) = $168
Max loss per share if Apple falls below $160
$3 (premium received from selling call option) - $1 (premium paid for buying put option) - $10 ( loss from owning Apple shares) = -$8
Scenario 1 – Apple trades to $175
P&L = $3 (premium received from selling call option) - $1 (premium paid for buying put option) + $5 ( gain from owning Apple shares) = $7
Scenario 2 – Apple trades to $165
P&L = $3 (premium received from selling call option) - $1 (premium paid for buying put option) - $5 ( Loss from owning Apple shares) = -$3
Uses of the Collar Option Strategy
The collar option strategy is yet another tactical option in a trader/investor’s toolkit to help hedge their positions in the portfolio over the short to medium term. If an investor holds a large position in a particular stock, they can construct a collar position to protect against short-term downside risks without letting go of the stock. The cost of purchasing the protective put option to hedge against the fall in price of the underlying asset can be offset from the sale of the covered call. If the cost of the put option is covered entirely by the sale of the call option, this can be called a zero-cost collar. If the cost of the put option is lower than the premium receive by the sale of the call option, then this works as a part hedge and part yield enhancement strategy.
As the collar options are more frequently used as a tactical strategy, a trader/investor has plenty of flexibility when employing this strategy and can choose to use this on some or all of their stock holdings in different market conditions.